Explain Different Classes of Ip Address
Class B networks have a first bit value of 1 and a second bit value of 0 in the first octet. While all IP addresses are made up of numbers or letters not all addresses are used for the same purpose.
Among them public and private addresses are based on their location of the network private which should be used inside a network while the public IP is used outside of a network.

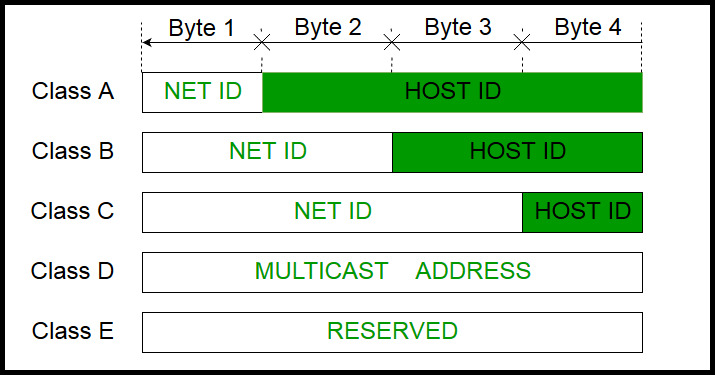
. A B or C corresponding to 8-bit 16-bit or 24-bit prefixes. Each class has a range of valid IP addresses. These classes are A B C D and E.
Class E is experimental so you can just forget about those too. The IP protocol defines five different address classes. These IP addresses can further be broken down into classes.
Let us see all these types of IP address in detail. IPv4 is the original version of IP addresses which is still widely used today in all computer networks. The first three classes vary the portion of the address devoted to the network ID and the host ID.
Class E is experimental so you can just forget about those too. A B C D and E. IPv4 Different Classes Although in IPv4 we have 4294967296 unique addresses.
IP address classes. The first three classes vary the portion of the address devoted to the network ID and the host ID. The classes of IPv4 addresses The different classes of the IPv4 address are the following.
Classes D and E are reserved for multicast and experimental purposes respectively. Public Private Static Dynamic. There are specific types of IP addresses.
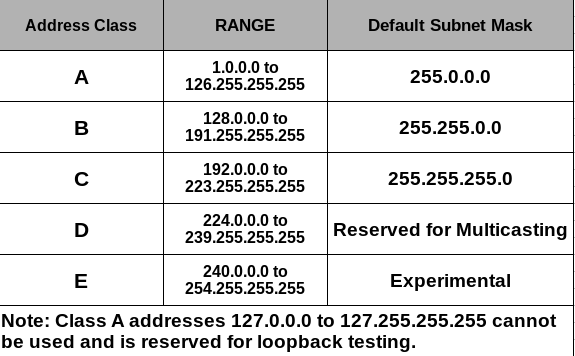
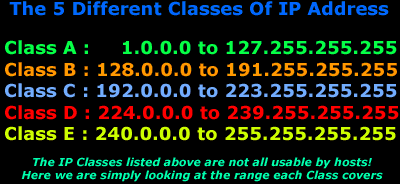
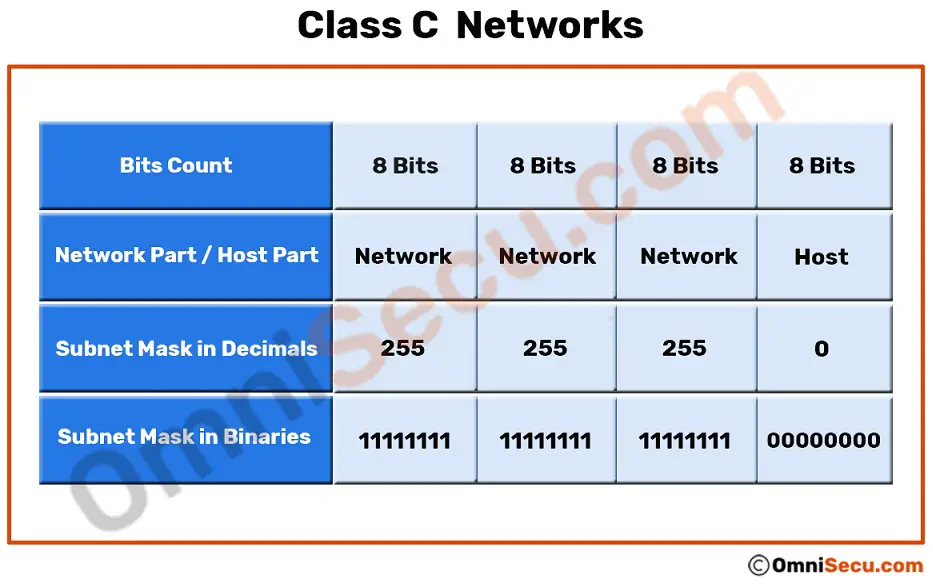
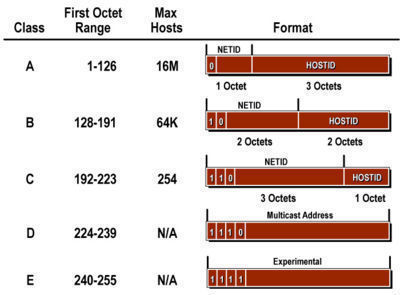
IP address classes Based on the following rules IP addresses are categorized into five classes. The first octet of Class C IP address has its first 3 bits set to 110 that is Class C IP addresses range from 19200x to 223255255x. A B C D and E.
There are three different types of IP addresses within this classification. Classes of IP addresses TCPIP defines five classes of IP addresses. It has first second and third bit value as 1 and the fourth bit as 0.
IP address with a first octet starts from 192-223. Unicast IP addresses are used to direct packets to a specific host. More 378 People Learned More Courses.
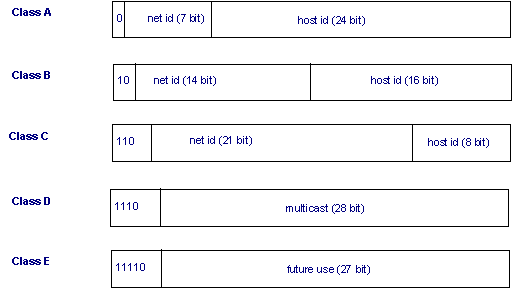
Each type of IP address can be an IPv4 address or an IPv6 address. The order of bits in the first octet determine the classes of IP address. In class B the first bit of the first byte always remains ON.
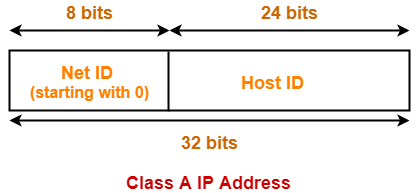
In class A the first bit of the first byte always remains OFF 0. Class C gives 2097152 2 21 Network addresses and 254 2 8 -2 Host addresses. Classes D and E are reserved for multicast and experimental purposes respectively.
There are 4 types of IP Addresses- Public Private Fixed and Dynamic. For humans the easiest way to distinguish between different address classes is to use the first decimal number in the IP address. But some of these addresses are not used for communication purpose.
A B C D and E. The IP protocol defines five different address classes. Class C IP address format is.
Class C is used for small to middle size networks. Class C networks have a first bit value of 1 second bit value of 1 and a third bit value of 0 in the first octet. The default subnet mask for Class C is 255255255x.
Class A B C D and E. Also one complete octet from Classes A B and C is used for Private IP addresses. The value of the first octet determines the class.
There are mainly four types of IP addresses. In order to deal with the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses. There were three address classes to chose from.
Classful Addressing The 32 bit IP address is divided into five sub-classes. Know more about Public and Private IP addresses. Each class occupies some part of the address space.
Among them public and private addresses are derived from their local network location which should be used within the network while public IP is used offline. Public IP address A public IP address is an Internet Protocol address encrypted by various serversdevices. A B C D and E.
We can find the class of an address when given the address in binary notation or dotted-decimal notation. In classful addressing the address space is divided into five classes. 1 Class A address 2 Class B address 3 Class C address 4 Class D address 5 Class E address Class A Address The first bit of the first octet is always set to zero.
Class A Class B Class C Class D Class E Each of these classes has a valid range of IP addresses. IP addresses from the first three classes A B and C can be used for host addresses. Class D is for multicast addresses which is something else entirely.
There are private IP addresses public IP addresses static IP addresses and dynamic IP addresses. 10 Different Types of IP Addresses Used in Computer Networks 1 IPv4. Classful Addressing The 32 bit IP address is divided into five sub-classes.
Multicast IP Addresses Multicast IP addresses are used for one-to-many communication. Class D is for multicast addresses which is something else entirely. So that the first octet ranges from 1 127.
These classes are A B C D E and their possible ranges can be seen in Figure 2 below. Unicast IP Addresses This is an address of a single interface which are used for one-to-one communication. Class A Class B Class C Class D Class E Each of these classes has a valid range of IP addresses.
The order of bits in the first octet determine the classes of IP address.

5 Classes Of Ip Address Archives Networkustad
Embeddedgeeks Network Ip Classes
Ip Address In Networking Classes Of Ip Address Gate Vidyalay
Ip Address In Networking Classes Of Ip Address Gate Vidyalay

Networking What Do Different Types Of Lan Ip Addresses Mean Super User

Different Classes Of Ip Address And Its Range And Subnet Mask Youtube
Internet Protocol Classes Network Host Id

5 Classes Of Ip Address Archives Networkustad
Introduction Of Classful Ip Addressing Geeksforgeeks
Class C Networks And Class C Ip Addresses

Introduction Of Classful Ip Addressing Geeksforgeeks

5 Different Classes Of Ip Address Explained With Examples Range Uses





Comments
Post a Comment